Lab-on-a-Chip Systems
Tuesday, 23 June 2015 22:09On this page you will find publications dealing with tiny cell or organ system developments on microchips. Aim of these developments is to connect all important human organs on the chip with smallest blood vessels to use them for toxicity testing in the future. Therefore this will be reduce or even terminate animal consumption.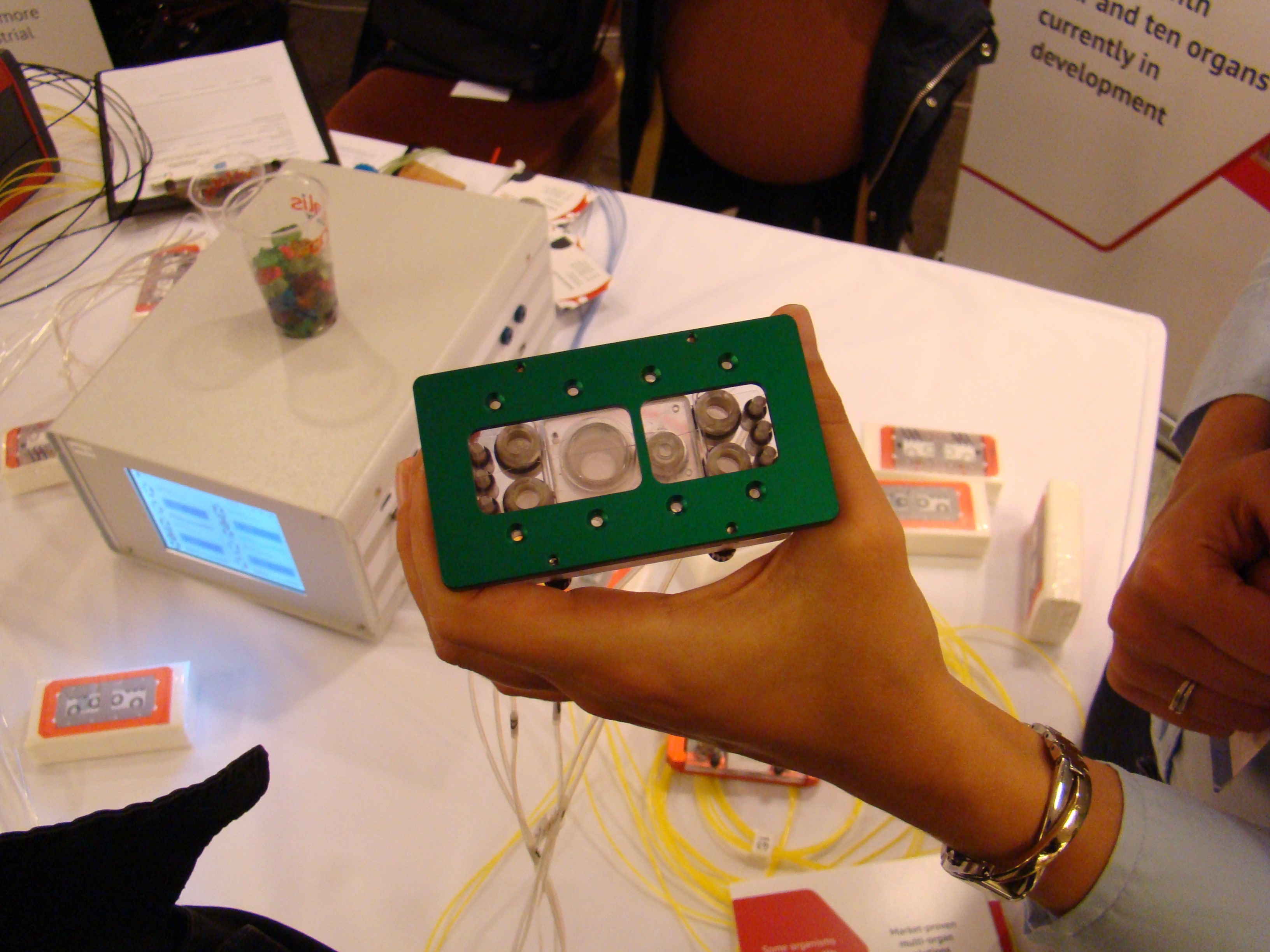
The chip systems can also be used in basic research, for instance to study human diseases with appropriate cell or organ systems expressing the disease phenomenon which are apllied to the chip.
The reader is also referred to our news releases and working groups on this topic.
Publications:
Johan U. Lind, Travis A. Busbee, Alexander D. Valentine et al. (2016): Instrumented cardiac microphysiological devices via multimaterial three-dimensional printing. Nature Materials.
Frey O., Misun P. M., Fluri D. A., Hengstler J. G. & Hierlemann A. (2014): Reconfigurable microfluidic hanging drop network for multi-tissue interaction and analysis. Nature Communications 5: 4250. doi: 10.1038/ncomms5250.
K. Schimek, M. Busek, S. Brincker, B. Groth, S. Hoffmann, R. Lauster, G. Lindner, A. Lorenz, U. Menzel, F. Sonntag, H. Walles, U. Marx and R. Horland (2013): Integrating biological vasculature into a multi-organ-chip microsystem; Lab Chip.
E. Materne, A. Tonevitsky and U. Marx (2013): Chip-based liver equivalents for toxicity testing - organotypicalness versus cost-efficient high throughput; Lab Chip.
I. Wagner, E. Materne, S. Brincker, U. Süßbier, C. Frädrich, M. Busek, F. Sonntag, D. Sakharov, E. Trushkin, A. Tonevitsky, R. Lauster, U. Marx (2013): A dynamic multi-organ-chip for long-term cultivation and substance testing proven by 3D human liver and skin tissue co-culture; Lab Chip.
B. Ataҫ, I. Wagner, R. Horland, R. Lauster, U. Marx, A. Tonevitsky, A. Azar, G. Lindner (2013): Skin and hair on-a-chip: in vitro skin models versus ex vivo tissue maintenance with dynamic perfusion; Lab Chip.
U. Marx, H. Walles, S. Hoffmann, G. Lindner, R. Horland, F. Sonntag, U. Klotzbach, D. Sakharov, A. Tonevitsky, R. Lauster (2012): 'Human-on-a-chip' developments: a translational cutting-edge alternative to systemic safety assessment and efficiency evaluation of substances in laboratory animals and man?; Alternatives to Lab Animals.
K.V. Gernaey, F. Baganz, E. Franco-Lara, F. Kensy, U. Krühne, M. Luebberstedt, U. Marx, E. Palmqvist, A. Schmid, F. Schubert, C.F. Mandenius (2012): Monitoring and control of microbioreactors: an expert opinion on development needs; Biotechnology Journal.
R. Horland, G. Lindner, I. Wagner, B. Atac, S. Hoffmann, M. Gruchow, F. Sonntag, U. Klotzbach, R. Lauster, U. Marx (2011): Human hair follicle equivalents in vitro for transplantation and chip-based substance testing; BMC Proceedings.
M. Pilarek, P. Neubauer, U. Marx (2011): Biological cardio-micro-pumps for microbioreactors and analytical micro-systems; Sensors and Actuators.
F. Sonntag, M. Gruchow, I. Wagner, G. Lindner, U. Marx (2011): Miniaturisierte humane organtypische Zell- und Gewebekulturen; BIOspektrum.
F. Sonntag, N. Schilling, K. Mader, M. Gruchow, U. Klotzbach, G. Lindner, R. Horland, I. Wagner, R. Lauster, S. Howitz, S. Hoffmann, U. Marx (2010): Design and prototyping of a chip-besed multi-micro-organoid culture system for substance testing, predictive to human (substance) exposure; Journal of Biotechnology.
Ground-breaking Technology
Monday, 23 June 2014 22:20With this page InVitro+Jobs offers information about "future-oriented developments". In this section, we'll focus on developments which have the potential to replace animal use in a particular field in the near future.
Innovative imaging methods could replace animal use (e.g. the use of non-human primates) with human-specific, non-invasive techniques in several fields of cognitive neuroscience.
Here you find literature sources that lead to the abstract.
The imaging techniques, however, require further testing to be accepted as animal replacement methods. Currently there are no studies reported and no evaluations or validations are known.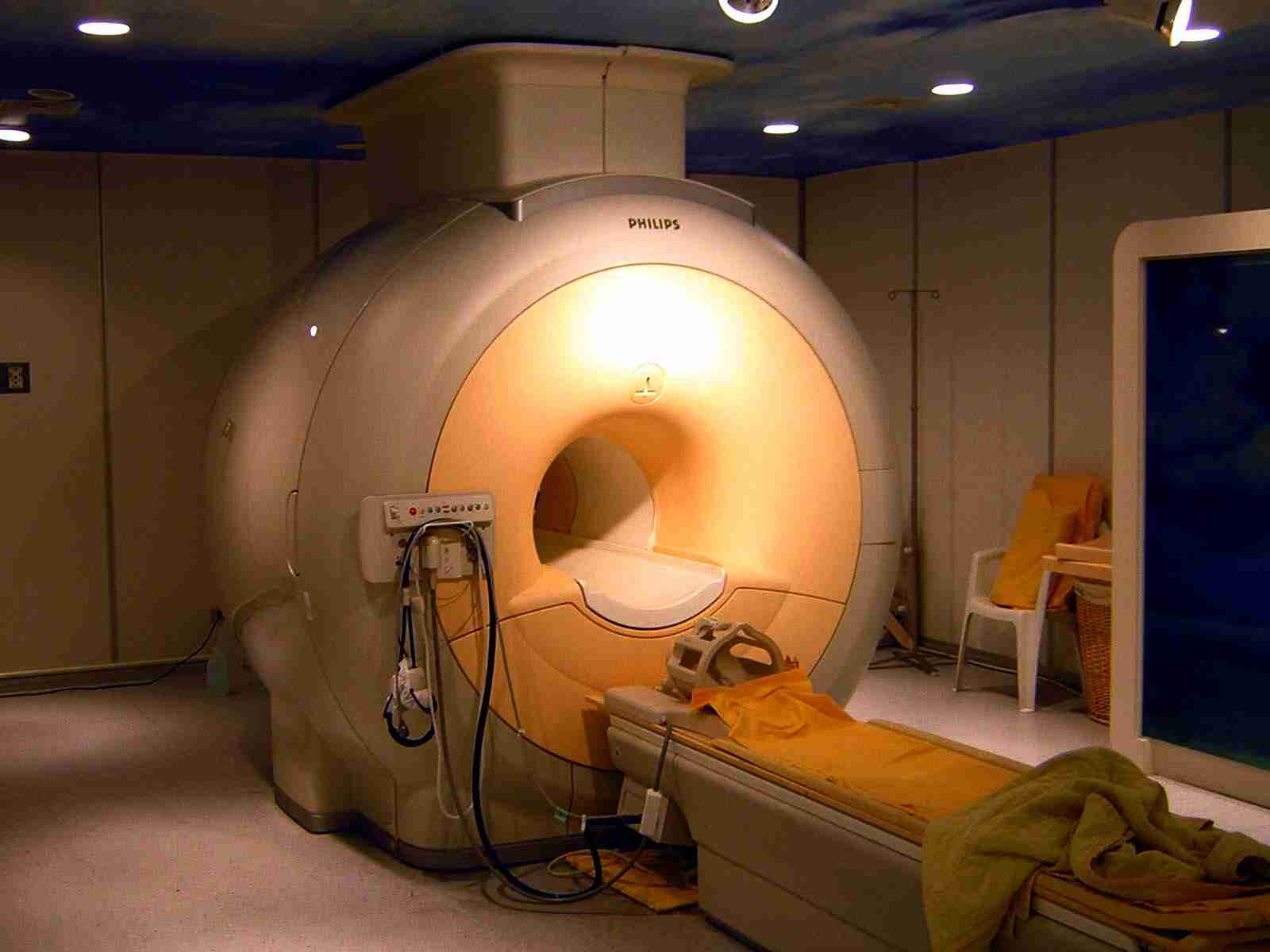
Photo: Kasuga Huang.
1. Imaging Methods
Aramesh, M., Forró, C., Dorwling-Carter, L., Lüchtefeld, I., Schlotter, T., Ihle, S. J., Shorubalko, I., Hosseini, V., Momotenko, D., Zambelli, T., Klotzsch, E. & Vörös, J. (2019).
Localized detection of ions and biomolecules with a force-controlled scanning nanopore microscope. Nature Nanotechnology, DOI: 10.1038/s41565-019-0493-z
Choi, Woo June & Wang, Ruikang K. (2015): Swept-source optical coherence tomography powered by a 1.3-μm vertical cavity surface emitting laser enables 2.3-mm-deep brain imaging in mice in vivo. J. Biomed. Opt. 20(10), 106004 (Oct 08, 2015). doi:10.1117/1.JBO.20.10.106004
Chojnacki, J., Staudt, T., Glass, B., Bingen, P., Engelhardt, J., Anders, M., Schneider, J., Müller, B., Hell, S. W. & Kräusslich, H.-G. (2012): Maturation-Dependent HIV-1 Surface Protein Redistribution Revealed by Fluorescence Nanoscopy. Science 338/6106: 524-528.
Connolly, C. G., Wu, J., Ho, T. C., Hoeft, F., Wolkowitz, O. Eisendrath, S., Frank, G., Hendren, R., Max, J. E., Paulus, M. P., Tapert, S. F. Banerjee, D., Simmons, A. N. & Yang, T. T. (2013): Resting-State Functional Connectivity of Subgenual Anterior Cingulate Cortex in Depressed Adolescents. Biol. Psychiatry.
de Winkel, K.N., Nesti, A., Ayaz, H. & Bülthoff, H. H. (2017): Neural correlates of decision making on whole body yaw rotation: an fNIRS study. Neuroscience Letters, Available online 13 June 2017
Derix, J., Yang, S., Lüsebrink, F., Fiederer, L. D. J., Schulze-Bonhage, A., Aertsen, A., Speck, O. and Ball, T. (2014): Visualization of the amygdalo–hippocampal border and its structural variability by 7T and 3T magnetic resonance imaging. Hum. Brain Mapp. Early View (Online Version of Record published before inclusion in an issue). DOI: 10.1002/hbm.22477
Downing, P., Liu, J., & Kanwisher, N. (2001): Testing cognitive models of visual attention with fMRI and MEG. Neuropsychologia, 39/12: 1329-1342.
EMPA (2022). Miniaturized Quantum Dot Infrared Spectrometer.
Espy, M., Matlachov, A., Volegov, P., Mosher, J.C., & Kraus, R.H., Jr. (2005): SQUID-based simultaneous detection of NMR and biomagnetic signals at ultra-low magnetic fields. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond., 15: 635-639.
Harrison, Ian F, Bernard Siow, Aisha B Akilo, Phoebe G Evans, Ozama Ismail, Yolanda Ohene, Payam Nahavandi, David L Thomas, Mark F Lythgoe & Jack A Wells (2018). Non-invasive imaging of CSF-mediated brain clearance pathways via assessment of perivascular fluid movement with DTI MRI. eLife 2018;7:e34028 doi: 10.7554/eLife.34028.
Haynes, J.D. & Rees, G. (2005): Predicting the orientation of invisible stimuli from activity in human primary visual cortex. Nat.Neurosci., 8/5: 686-691.
Hipp, L., Beer, J., Kuchler, O., Reisser, M., Sinske, D., Michaelis, J., Gebhardt, J.C.M. & Knöll, B. (2019). Single-molecule imaging of the transcription factor SRF reveals prolonged chromatin-binding kinetics upon cell stimulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 116(3): 880-889.
Höfner, N., Albrecht, H. H., Cassara, A. M., Curio, G., Hartwig, S., Haueisen, J., Hilschenz, I., Korber, R., Martens, S., Scheer, H. J., Voigt, J., Trahms, L., & Burghoff, M. (2011): Are brain currents detectable by means of low-field NMR? A phantom study. Magn Reson. Imaging 29/10: 1365-1373.
Kaiplavil, Sreekumar & Mandelis, Andreas (2014): Truncated-correlation photothermal coherence tomography for deep subsurface analysis. Nature Photonics. doi:10.1038/nphoton.2014.111
Kamitani, Y. & Tong, F. (2006): Decoding seen and attended motion directions from activity in the human visual cortex. Curr.Biol, 16/11: 1096-1102.
Karampinos, Dimitrios C., Claussnitzer, Melina & Hauner, Hans (2022): Transcriptome and fatty-acid signatures of adipocyte hypertrophy and its non-invasive MR-based characterization in human adipose tissue. EBioMedicine.
Klippel, S., Döpfert, J., Jabadurai Jayapaul, J., Kunth, M., Rossella, F., Schnurr, M., Witte, C., Freund, C. & Schröder, L. (2013: Cell tracking with Caged Xenon: Using Cryptophanes as MRI Reporters upon Cellular Internalization.(Epub ahead of print) DOI:10.1002/anie.201307290
König, K & Ostendorf, A (Eds.): Optically Induced Nanostructures. Biomedical and Technical Applications. Verlag DeGruyter (2015).
Kraus, R.H., Jr., Volegov, P., Matlachov, A., & Espy, M. (2008): Toward direct neural current imaging by resonant mechanisms at ultra-low field. Neuroimage., 39/1: 310-317.
Lavery, L., Merkle, A. & Gelb, J. (2015). 3D X-ray Microscopy: A New High Resolution Tomographic Technology for Biological Specimens. Microsc. Microanal. 21 (Suppl 3).
Le Bihan, D., Mangin, J.-F., Poupon, C., Clark, C. A., Pappata, S., Molko, N., & Chabriat, H. (2001): Diffusion Tensor Imaging: Concepts and Applications. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging. 13: 534–546.
Lee, M. H., Smyser, C. D. & Shimony, J. S. (2012): Resting-State fMRI: A Review of Methods and Clinical Applications. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 10.3174/ajnr.A3263
Lee, T, Cai, LX, Lelyveld, VS, Aviad Hai & Alan Jasanoff (2014): Molecular-Level Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Dopaminergic Signaling. Science 344: 533-535.
Li, Y., et al. (2020). Multifocal photoacoustic microscopy using a single-element ultrasonic transducer through an ergodic relay. Light: Science & Applications. doi.org/10.1038/s41377-020-00372-x.
Liangzhong Xiang, Bo Wang, Lijun Ji & Huabei Jiang (2013): 4-D Photoacoustic Tomography. Scientific Reports 3 : 1113, DOI: 10.1038/srep01113
V. Loconte, J.-H. Chen, M. Cortese, A. Ekman, M. A. Le Gros, C. Larabell, R. Bartenschlager, V. Weinhardt; "Using soft X-ray tomography for rapid whole-cell quantitative imaging of SARS-CoV-2-infected cells"; Cell Reports Methods; Vol. 1, Issue 7, 22 November 2021, 100117
Loretz, M., Rosskopf, T., Boss, J.M., Pezzagna, S., Meijer, J. & C. L. Degen (2014): Single-proton spin detection by diamond magnetometry. Science Express Reports. doi: 10.1126/science.1259464
-> New: Nanda, S., Calderon, A., Sachan, A. et al. Rho GTPase activity crosstalk mediated by Arhgef11 and Arhgef12 coordinates cell protrusion-retraction cycles. Nat Commun 14, 8356 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-43875-y
Nielles-Vallespin, S., Mekkaoui,C., Gatehouse, P., Reese, T. G., Keegan, J., Ferreira, P. F., Collins, S., Speier, P., Feiweier, T., de Silva, R., Jackowski, M. P., Pennell, D. J., Sosnovik, D. E. & Firmin, D. (2013): In Vivo Diffusion Tensor MRI of the Human Heart: Reproducibility of Breath-Hold and Navigator-Based Approaches. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine. 70:454–465.
-> New: Reznik D, Trampel R, Weiskopf N, Witter MP, Doeller CF. (2023). Dissociating distinct cortical networks associated with subregions of the human medial temporal lobe using precision neuroimaging. Neuron. Jun 23: S0896-6273(23)00402-6. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2023.05.029. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 37390820.
Schindler, A. & Bartels, A. (2013): Parietal Cortex Codes for Egocentric Space beyond the Field of View. Current Biology 23, 1–6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2012.11.06011.060
Schneider, J., Zahn, J., Maglione, M., Sigrist, S. J., Marquard, J., Chojnacki, J., Kräusslich, H.-G., Sahl, S. J., Engelhardt, J. & Hell, S. W. (2015): Ultrafast, temporally stochastic STED nanoscopy of millisecond dynamics. Nature Methods 2015, 10.1038/nmeth.3481
Oliver Schoppe, Chenchen Pan, Javier Coronel, Hongcheng Mai, Zhouyi Rong, Mihail Ivilinov Todorov, Annemarie Müskes, Fernando Navarro, Hongwei Li, Ali Ertürk, Bjoern H. Menze; "Deep learning-enabled multi-organ segmentation in whole-body mouse scans"; Nature communications.
Shibata, M., Uchihashi, T., Ando, T. & Yasuda, R. (2015): Long-tip high-speed atomic force microscopy for nanometer-scale imaging in live cells. SCIENTIFIC REPORTS 5: 8724, DOI: 10.1038/srep08724.
-> New: Speiser, A., Müller, LR., Hoess, P. et al. Deep learning enables fast and dense single-molecule localization with high accuracy. Nat Methods (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41592-021-01236-x
-> New: Sunbul, M., Lackner, J., Martin, A. et al. (2021). Super-resolution RNA imaging using a rhodamine-binding aptamer with fast exchange kinetics. Nat Biotechnol (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-020-00794-3
Thunemann M, Schörg BF, Feil S, Lin Y, Voelkl J, Golla M, Vachaviolos A, Kohlhofer U, Quintanilla-Martinez L, Olbrich M, Ehrlichmann W, Reischl G, Griessinger CM, Langer HF, Gawaz M, Lang F, Schäfers M, Kneilling M, Pichler BJ, Feil R. (2017): Cre/lox-assisted non-invasive in vivo tracking of specific cell populations by positron emission tomography. Nature Communications. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-017-00482-y.
Tong, F. Harrison S. A., Dewey, J. A., Kamitani, Y (2013): Relationship between BOLD amplitude and pattern classification of orientation-selective activity in the human visual cortex. NeuroImage 63 (2012) 1212–1222.
-> New: Wu, Y., Han, X., Su, Y. et al. Multiview confocal super-resolution microscopy. Nature (2021). 
Photo: Paul Wicks.
2. Non-invasive Brain-Computer Interface
-> New: Kraus D, Naros G, Guggenberger R, Leão MT, Ziemann U, Gharabaghi A. (2018): Recruitment of additional corticospinal pathways in the human brain with state-dependent paired associative stimulation. J Neurosci.
Kraus D, Naros G, Bauer R, Leão MT, Ziemann U, Gharabaghi A. (2016): Brain-robot interface driven plasticity: Distributed modulation of corticospinal excitability. Neuroimage 125: 522-532.
-> New: Nann, M., Cohen, L. G., Deecke L. & Soekadar, S. R. (2019). To jump or not to jump – The Bereitschaftspotential required to jump into 192-meter abyss. Sci Rep. 9: 2243. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-38447-w.
Quandt, F., Reichert, C., Hinrichs, H., Heinze, H.J., Knight, R.T., & Rieger, J. W. (2012): Single trial discrimination of individual finger movements on one hand: a combined MEG and EEG study. Neuroimage., 59/4: 3316-3324.
Waldert, S., Preissl, H., Demandt, E., Braun, C., Birbaumer, N., Aertsen, A., & Mehring, C. (2008): Hand movement direction decoded from MEG and EEG. J Neurosci., 28/4: 1000-1008.
3. Non-Invasive Procedures for Brain Stimulation
Tufail, Y., Matyushov, A., Baldwin, N., Tauchmann, M. L., Georges, J., Yoshihiro, A., Tillery, S. I., & Tyler, W. J. (2010): Transcranial pulsed ultrasound stimulates intact brain circuits. Neuron, 66/5: 681-694.
Photo: Sven Hoppe, Fotolia.com
4. Human-specific Disease Models (Diseases-in-a-dish)
Callaway, E. (2011): Cells snag top modelling job. Nature 469/7330: 279.
Se Hoon Choi, Young Hye Kim, Matthias Hebisch, Christopher Sliwinski, Seungkyu Lee, Carla D’Avanzo, Hechao Chen, Basavaraj Hooli, Caroline Asselin, Julien Muffat, Justin B. Klee, Can Zhang, Brian J. Wainger, Michael Peitz, Dora M. Kovacs, Clifford J. Woolf, Steven L. Wagner, Rudolph E. Tanzi & Doo Yeon Kim (2014): A three-dimensional human neural cell culture model of Alzheimer’s disease. doi:10.1038/nature13800
-> New: Dekkers, JF, Berkers, G, Kruisselbrink, E, et al. (2016): Characterizing responses to CFTR-modulating drugs using rectal organoids derived from subjects with cystic fibrosis. Science 8/344.
-> New: Graffmann N, Ring S, Kawala MA, Wruck W, Ncube A, Trompeter HI, et al. (2016): Modelling NAFLD with human pluripotent stem cell derived immature hepatocyte like cells reveals activation of PLIN2 and confirms regulatory functions of PPARalpha. Stem cells and development.
D. Huh, D. C. Leslie, B. D. Matthews, J. P. Fraser, S. Jurek, G. A. Hamilton, K. S. Thorneloe, M. A. McAlexander, D. E. Ingber, A Human Disease Model of Drug Toxicity–Induced Pulmonary Edema in a Lung-on-a-Chip Microdevice. Sci. Transl. Med. 4, 159ra147 (2012).
Itzhaki, I., Maizels, L., Huber, I., Zwi-Dantsis, L., Caspi, O., Winterstern, A., Feldman, O., Gepstein, A., Arbel, G., Hammerman, H., Boulos, M., & Gepstein, L. (2011): Modelling the long QT syndrome with induced pluripotent stem cells. Nature, 471/7337: 225-229.
Jerome Mertens, Apuã C.M. Paquola, Manching Ku, Emily Hatch, Lena Böhnke, Shauheen Ladjevardi, Sean McGrath, Benjamin Campbell, Hyungjun Lee, Joseph R. Herdy, J. Tiago Goncalves, Tomohisa Toda, Yongsung Kim, Jürgen Winkler, Jun Yao, Martin Hetzer, and Fred H. Gage (2015): Directly Reprogrammed Human Neurons Retain Aging-Associated Transcriptomic Signatures and Reveal Age-Related Nucleocytoplasmic Defects. Cell Stem Cell DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.stem.2015.09.001
Moretti, A., Bellin, M., Welling, A., Jung, C.B., Lam, J.T., Bott-Flugel, L., Dorn, T., Goedel, A., Hohnke, C., Hofmann, F., Seyfarth, M., Sinnecker, D., Schomig, A., & Laugwitz, K.L. (2010): Patient-specific induced pluripotent stem-cell models for long-QT syndrome. N Engl. J Med 363/15: 1397-1409.
Nguyen, D.-H. T., Stapleton, S. C., Yang, M. T., Cha, S. S., Choi, C. K., Galie, P. A. & Chen, C. S. (2013): Biomimetic model to reconstitute angiogenic sprouting morphogenesis in vitro. PNAS 110/17: 6712-6717.
-> New: Christos Papadimitriou, Hilal Celikkaya, Mehmet I. Cosacak, Violeta Mashkaryan, Laura Bray, Prabesh Bhattarai, Kerstin Brandt, Heike Hollak, Xin Chen, Shuijin He, Christopher L. Antos, Weilin Lin, Alvin Kuriakose Thomas, Andreas Dahl, Thomas Kurth, Jens Friedrichs, Yixin Zhang, Uwe Freudenberg, Carsten Werner & Caghan Kizil (2018). 3D Culture Method for Alzheimer’s Disease Modeling Reveals Interleukin-4 Rescues Ab42-Induced Loss of Human Neural Stem Cell Plasticity. Developmental Cell 46: 85–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2018.06.005.
Takahashi, K., Tanabe, K., Ohnuki, M., Narita, M., Ichisaka, T., Tomoda, K., & Yamanaka, S. (2007): Induction of pluripotent stem cells from adult human fibroblasts by defined factors. Cell, 131/5: 861-872.
Wang, G., McCain, M., et. al. (2014): Modeling the mitochondrial cardiomyopathy of Barth syndrome with iPSC and heart-on-a-chip technologies. Nature Medicine.
5. Microfluidic systems
-> Neu: Chen, H.J., Miller, P. & Shuler, M. L. (2018). A pumpless body-on-a-chip model using a primary culture of human intestinal cells and a 3D culture of liver cells. Lab Chip. 2018 Jun 8. doi: 10.1039/c8lc00111a.
Huh, D., Matthews, B. D., Mammoto, A., Montoya-Zavala, M., Hsin, H.Y., & Ingber, D. E. (2010): Reconstituting organ-level lung functions on a chip. Science, 328/5986: 1662-1668.
Huh, D., Hamilton, G. A., & Ingber, D. E. (2011): From 3D cell culture to organs-on-chips. Trends Cell Biol, 21/12: 745-754.
Neuzil, P. et al. (2012): Revisiting lab-on-a-chip technology for drug discovery. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 11: 620 - 32.
-> Neu: Friedrich Schuler, Frank Schwemmer, Martin Trotter, Simon Wadle, Roland Zengerle, Felix von Stetten und Nils Paust (2015): Centrifugal step emulsification applied for absolute quantification of nucleic acids by digital droplet RPA. Lab Chip, 2015,15, 2759-2766. DOI: 10.1039/C5LC00291E
Tsai, M., Kita, A., Leach, J., Rounsevell, R., Huang, J. N., Moake, J., Ware, R. E., Fletcher, D. A., & Lam, W. A. (2012): In vitro modeling of the microvascular occlusion and thrombosis that occur in hematologic diseases using microfluidic technology. J Clin Invest, 122/1: 408-418.


 Dr. rer. nat.
Dr. rer. nat. Menschen für Tierrechte - Tierversuchsgegner Rheinland-Pfalz e.V.
Menschen für Tierrechte - Tierversuchsgegner Rheinland-Pfalz e.V.